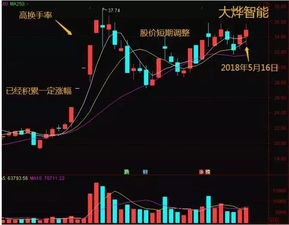
股市的换手率
Understanding Stock Turnover Rates Across Different Phases
Stock turnover rate, also known as inventory turnover, is a critical metric used to assess how efficiently a company manages its inventory. In the context of stocks, turnover rate refers to how frequently shares of a company are bought and sold within a specific period. The turnover rate can vary significantly across different phases or stages in the stock market cycle. Let's explore the typical turnover rates observed in various phases:
1. Early Growth Phase:
Description:
During this phase, a company is in its initial stages of growth, often characterized by high volatility and speculative trading.
Turnover Rate:
The turnover rate tends to be relatively high as investors actively buy and sell shares based on expectations and news about the company's potential growth prospects. 2. Mature Growth Phase:
Description:
In this phase, the company experiences steady growth, and its business model proves successful.
Turnover Rate:
While still significant, the turnover rate might start to stabilize compared to the early growth phase as investors hold onto their positions for longer periods, confident in the company's performance. 3. Plateau Phase:
Description:
The company reaches a point where its growth rate slows down, and it enters a period of stability.
Turnover Rate:
The turnover rate typically decreases during this phase as investors become more riskaverse and seek stable, dividendpaying stocks. Longterm investors dominate the market, resulting in fewer trades. 4. Decline Phase:
Description:
The company faces challenges such as declining sales, profitability, or technological obsolescence.
Turnover Rate:
Turnover rate can vary widely during this phase. It may increase as traders attempt to profit from shortselling or decrease as longterm investors exit their positions. 5. Recovery Phase:
Description:
After a period of decline, the company implements strategic changes to reverse its fortunes and regain market confidence.
Turnover Rate:
Turnover rate may increase as traders anticipate a turnaround and buy shares at discounted prices. Longterm investors cautiously monitor the company's progress, leading to mixed trading activity. 6. Maturity Phase:
Description:
The company achieves stability and maturity in its operations, with consistent performance and established market presence.
Turnover Rate:
Turnover rate tends to stabilize at a lower level compared to earlier phases. Investors focus on dividend income and capital preservation rather than rapid growth, leading to fewer trades.Recommendations for Investors:
Understand the Phase:
Recognizing which phase a company is in can help investors make informed decisions. Early growth phases offer potential for high returns but come with higher risks, while mature phases offer stability but limited growth prospects.
Consider Investment Horizon:
Shortterm traders may thrive in phases with high turnover rates, while longterm investors may prefer phases characterized by stability and lower turnover.
Diversify Portfolio:
Diversification across companies in different phases can mitigate risk and capitalize on opportunities across various market conditions.In conclusion, stock turnover rates vary across different phases of a company's lifecycle, reflecting changing investor sentiments, market dynamics, and business performance. Understanding these phases and their associated turnover rates is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the stock market effectively.
Considering the diverse phases of stock market cycles, this overview provides insights into how turnover rates fluctuate across different stages, helping investors tailor their strategies accordingly. If you have further inquiries or need additional details on any specific phase, feel free to ask!
免责声明:本网站部分内容由用户上传,若侵犯您权益,请联系我们,谢谢!联系QQ:2760375052